A hexagram (Greek) or sexagram (Latin) is a six-pointed geometric star figure with the Schläfli symbol {6/2}, 2{3}, or {{3}}. It is the compound of two equilateral triangles. The intersection is a regular hexagon.
It is used in historical, religious and cultural contexts, for example in Hanafism,[1] Jewish identity, Hinduism and occultism.
Contents
[hide]- 1Group theory
- 2Construction by compass and a straight edge
- 3Origins and shape
- 4Usage in Asian religions
- 5Usage by the Abrahamic religions
- 6Usage in heraldry
- 7Usage in theosophy
- 8Usage in Occultism
- 9Usage in Freemasonry
- 10Other uses
- 11Other hexagrams
- 12See also
- 13Footnotes
- 14References
- 15External links
Group theory[edit]
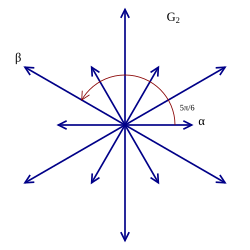
In mathematics, the root system for the simple Lie group G2 is in the form of a hexagram, with 6 long roots and 6 short roots.


No comments:
Post a Comment