15 Uncanny Examples of the Golden Ratio in Nature

The famous Fibonacci sequence has captivated mathematicians, artists,
designers, and scientists for centuries. Also known as the Golden Ratio,
its ubiquity and astounding functionality in nature suggests its
importance as a fundamental characteristic of the Universe.
We've talked about the Fibonacci series and the Golden ratio before,
but it's worth a quick review. The Fibonacci sequence starts like this:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55 and so on forever. Each number is
the sum of the two numbers that precede it. It's a simple pattern, but
it appears to be a kind of built-in numbering system to the cosmos. Here
are 15 astounding examples of phi in nature.
Leonardo
Fibonacci came up with the sequence when calculating the ideal expansion
pairs of rabbits over the course of one year. Today, its emergent
patterns and ratios (phi = 1.61803...) can be seen from the microscale
to the macroscale, and right through to biological systems and inanimate
objects. While the Golden Ratio doesn't account for every structure or pattern in the universe, it's certainly a major player. Here are some examples.
1. Flower petals

The number
of petals in a flower consistently follows the Fibonacci sequence.
Famous examples include the lily, which has three petals, buttercups,
which have five (pictured at left), the chicory's 21, the daisy's 34,
and so on. Phi appears in petals on account of the ideal packing
arrangement as selected by Darwinian processes; each petal is placed at
0.618034 per turn (out of a 360° circle) allowing for the best possible
exposure to sunlight and other factors.
2. Seed heads
The head of
a flower is also subject to Fibonaccian processes. Typically, seeds are
produced at the center, and then migrate towards the outside to fill
all the space. Sunflowers provide a great example of these spiraling
patterns.
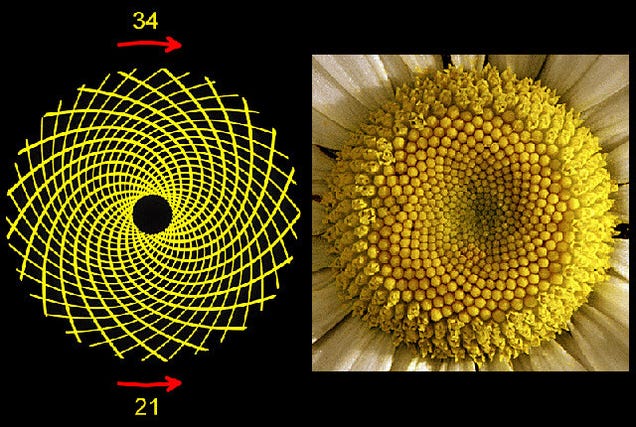
In some
cases, the seed heads are so tightly packed that total number can get
quite high — as many as 144 or more. And when counting these spirals,
the total tends to match a Fibonacci number. Interestingly, a highly
irrational number is required to optimize filling (namely one that will
not be well represented by a fraction). Phi fits the bill rather nicely.
3. Pinecones
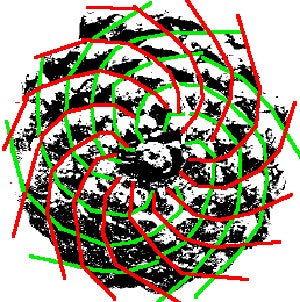
Similarly,
the seed pods on a pinecone are arranged in a spiral pattern. Each cone
consists of a pair of spirals, each one spiraling upwards in opposing
directions. The number of steps will almost always match a pair of
consecutive Fibonacci numbers. For example, a 3-5 cone is a cone which
meets at the back after three steps along the left spiral, and five
steps along the right.
4. Fruits and Vegetables
Likewise, similar spiraling patterns can be found on pineapples and cauliflower.
5. Tree branches
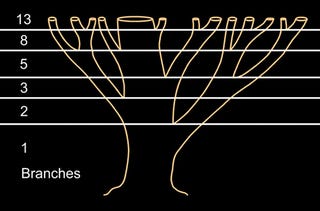
The
Fibonacci sequence can also be seen in the way tree branches form or
split. A main trunk will grow until it produces a branch, which creates
two growth points. Then, one of the new stems branches into two, while
the other one lies dormant. This pattern of branching is repeated for
each of the new stems. A good example is the sneezewort. Root systems
and even algae exhibit this pattern.
6. Shells
The unique
properties of the Golden Rectangle provides another example. This shape,
a rectangle in which the ratio of the sides a/b is equal to the golden
mean (phi), can result in a nesting process that can be repeated into
infinity — and which takes on the form of a spiral. It's call the
logarithmic spiral, and it abounds in nature.
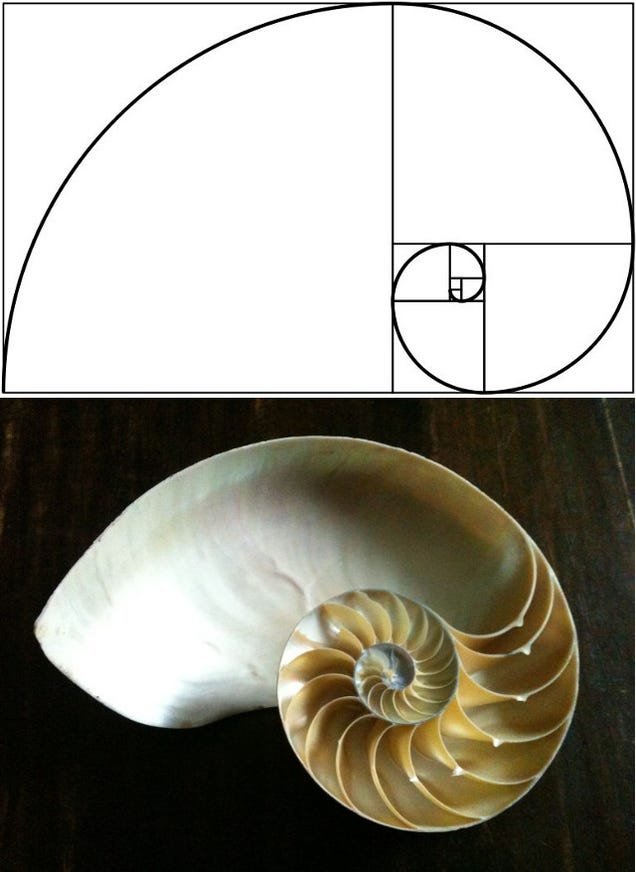
Snail
shells and nautilus shells follow the logarithmic spiral, as does the
cochlea of the inner ear. It can also be seen in the horns of certain
goats, and the shape of certain spider's webs.
7. Spiral Galaxies

Not
surprisingly, spiral galaxies also follow the familiar Fibonacci
pattern. The Milky Way has several spiral arms, each of them a
logarithmic spiral of about 12 degrees. As an interesting aside, spiral
galaxies appear to defy Newtonian physics. As early as 1925, astronomers
realized that, since the angular speed of rotation of the galactic disk
varies with distance from the center, the radial arms should become
curved as galaxies rotate. Subsequently, after a few rotations, spiral
arms should start to wind around a galaxy. But they don't — hence the
so-called winding problem.
The stars on the outside, it would seem, move at a velocity higher than
expected — a unique trait of the cosmos that helps preserve its shape.
8. Hurricanes
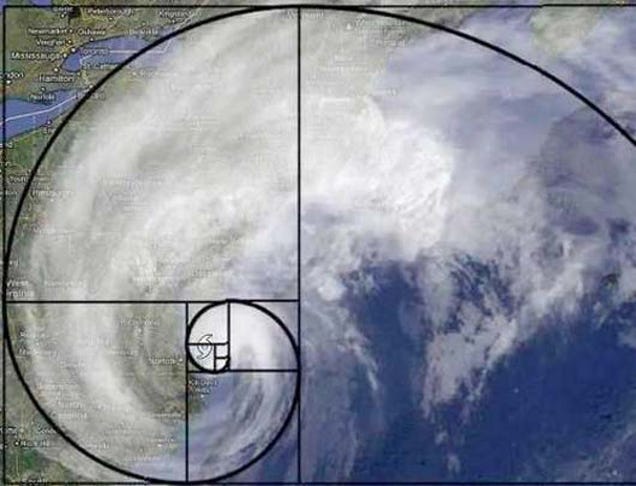
9. Faces

Faces,
both human and nonhuman, abound with examples of the Golden Ratio. The
mouth and nose are each positioned at golden sections of the distance
between the eyes and the bottom of the chin. Similar proportions can
been seen from the side, and even the eye and ear itself (which follows
along a spiral).
It's worth
noting that every person's body is different, but that averages across
populations tend towards phi. It has also been said that the more
closely our proportions adhere to phi, the more "attractive" those
traits are perceived. As an example, the most "beautiful" smiles are
those in which central incisors are 1.618 wider than the lateral
incisors, which are 1.618 wider than canines, and so on. It's quite
possible that, from an evo-psych perspective, that we are primed to like
physical forms that adhere to the golden ratio — a potential indicator
of reproductive fitness and health.
10. Fingers
Looking at
the length of our fingers, each section — from the tip of the base to
the wrist — is larger than the preceding one by roughly the ratio of
phi.
11. Animal bodies
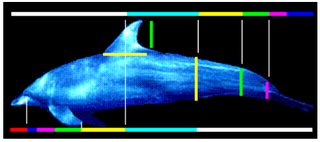
Even our
bodies exhibit proportions that are consistent with Fibonacci numbers.
For example, the measurement from the navel to the floor and the top of
the head to the navel is the golden ratio. Animal bodies exhibit similar
tendencies, including dolphins (the eye, fins and tail all fall at
Golden Sections), starfish, sand dollars, sea urchins, ants, and honey
bees.
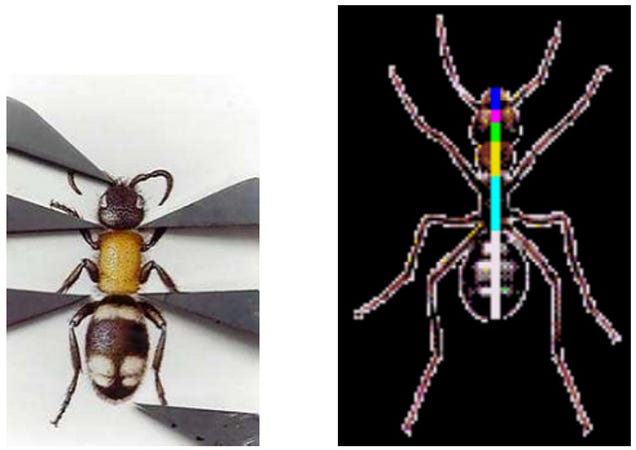
12. Reproductive dynamics

Speaking
of honey bees, they follow Fibonacci in other interesting ways. The most
profound example is by dividing the number of females in a colony by
the number of males (females always outnumber males). The answer is
typically something very close to 1.618. In addition, the family tree of
honey bees also follows the familiar pattern. Males have one parent (a
female), whereas females have two (a female and male). Thus, when it
comes to the family tree, males have 2, 3, 5, and 8 grandparents,
great-grandparents, gr-gr-grandparents, and gr-gr-gr-grandparents
respectively. Following the same pattern, females have 2, 3, 5, 8, 13,
and so on. And as noted, bee physiology also follows along the Golden
Curve rather nicely.
13. Animal fight patterns
When a hawk
approaches its prey, its sharpest view is at an angle to their
direction of flight — an angle that's the same as the spiral's pitch.
14. The uterus
According
to Jasper Veguts, a gynaecologist at the University Hospital Leuven in
Belgium, doctors can tell whether a uterus looks normal and healthy
based on its relative dimensions — dimensions that approximate the golden ratio. From the Guardian:
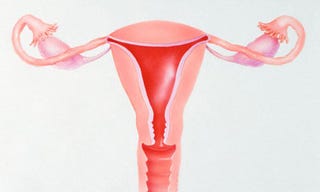
Over the last few months he has measured the uteruses of 5,000 women using ultrasound and drawn up a table of the average ratio of a uterus's length to its width for different age bands.The data shows that this ratio is about 2 at birth and then it steadily decreases through a woman's life to 1.46 when she is in old age.Dr Verguts was thrilled to discover that when women are at their most fertile, between the ages of 16 and 20, the ratio of length to width of a uterus is 1.6 – a very good approximation to the golden ratio."This is the first time anyone has looked at this, so I am pleased it turned out so nicely," he said.
15. DNA molecules
Even the
microscopic realm is not immune to Fibonacci. The DNA molecule measures
34 angstroms long by 21 angstroms wide for each full cycle of its double
helix spiral. These numbers, 34 and 21, are numbers in the Fibonacci
series, and their ratio 1.6190476 closely approximates Phi, 1.6180339.
Thanks to Calvin Dvorsky for helping with the article!
Sources and images: Top: Loskutnikov/Shutterstock; Buttercup: motorolka/shutterstock, ThinkQuest, Shell, Galaxy: FabulousFibonacci, American Museum of Natural History and here, honey bee, Hurricane: MNN, Faces: Goldennumber and here, DNA.

No comments:
Post a Comment