The earth back 66 million years ago was different, without mentioning the presence or absence of dinos..........for one, there were no polar caps.........
As evidence of that event................they have the crater itself...........and from rock sediments dating back to 66 million years ago...........from parts of the earth far from Old Mexico............matches the time period, etc..............
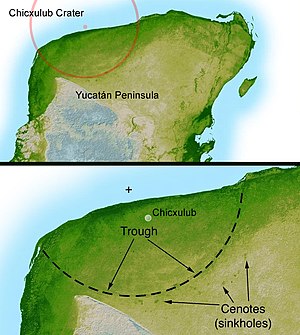
This is supposedly the crater in sunny Mexico formed by said 6 mile in diameter shepherical rock....................
Chicxulub crater
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For the town and municipality, see Chicxulub, Yucatán.
The Chicxulub crater (/ˈtʃiːkʃʉluːb/; Mayan pronunciation: [tʃʼikʃuluɓ]) is a prehistoric impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico.[2] Its center is located near the town of Chicxulub, after which the crater is named.[3] The age of the Chicxulub asteroid impact and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K–Pg boundary) coincide precisely.[4] The crater is more than 180 kilometres (110 mi) in diameter and 20 km (12 mi) in depth, making the feature one of the largest confirmed impact structures on Earth; the impacting bolide that formed the crater was at least 10 km (6 mi) in diameter.
The crater was discovered by Antonio Camargo and Glen Penfield, geophysicists who had been looking for petroleum in the Yucatán during the late 1970s. Penfield was initially unable to obtain evidence that the geological feature was a crater, and gave up his search. Through contact with Alan Hildebrand, Penfield obtained samples that suggested it was an impact feature. Evidence for the impact origin of the crater includes shocked quartz, a gravity anomaly, and tektites in surrounding areas.
The age of the rocks marked by the impact shows that this impact structure dates from roughly 66 million years ago, the end of the Cretaceous period, and the start of the Paleogene period. It coincides with the K-Pg boundary, the geological boundary between the Cretaceous and Paleogene. The impact associated with the crater is thus implicated in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, including the worldwide extinction of non-avian dinosaurs. This conclusion has been the source of controversy. In March 2010, 41 experts from many countries reviewed the available evidence: 20 years' worth of data spanning a variety of fields. They concluded that the impact at Chicxulub triggered the mass extinctions at the K–Pg boundary.[5
No comments:
Post a Comment