Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event,[a] formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) extinction,[b] was a mass extinction of some three-quarters of plant and animal species on Earth—including all non-avian dinosaurs—that occurred over a geologically short period of time 66 million years ago.[2][3] It marked the end of the Cretaceous period and with it, the entire Mesozoic Era, opening theCenozoic Era which continues today.
In the geologic record, the K–Pg event is marked by a thin layer of sediment called the K–Pg boundary, which can be found throughout the world in marine and terrestrial rocks. The boundary clay shows high levels of the metal iridium, which is rare in the Earth's crust but abundant in asteroids.
As originally proposed by a team of scientists led by Luis Alvarez, it is now generally believed that the K–Pg extinction was triggered by a massive comet/asteroid impact and its catastrophic effects on the global environment, including a lingering impact winter that made it impossible for plants and plankton to carry out photosynthesis.[4][5] The impact hypothesis was bolstered by the discovery of the 180-kilometre-wide (112 mi) Chicxulub crater in the Gulf of Mexico in the early 1990s,[6] which provided conclusive evidence that the K–Pg boundary clay represented debris from an asteroid impact.[7] The fact that the extinctions occurred at the same time as the impact provides strong situational evidence that the K–Pg extinction was caused by the asteroid.[7] However, some scientists maintain the extinction was caused or exacerbated by other factors, such as volcanic eruptions,[8] climate change, or sea level change, separately or together.
A wide range of species perished in the K–Pg extinction. The most well-known victims are the non-avian dinosaurs. However, the extinction also destroyed a plethora of other terrestrial organisms, including but not limited to, certain mammals, pterosaurs, birds,[9] lizards,[10] insects,[11][12] and plants.[13] In the oceans, the K–Pg extinction devastated the giant marine lizards (Mosasauridae), plesiosaurs, fish,[14]sharks, mollusks (especially ammonites) and many species of plankton. It is estimated that 75% or more of all species on Earth vanished.[15] Yet the devastation caused by the extinction also provided evolutionary opportunities. In the wake of the extinction, many groups underwent remarkable adaptive radiations — a sudden and prolific divergence into new forms and species within the disrupted and emptied ecological niches resulting from the event. Mammals in particular diversified in the Paleogene,[16] producing new forms such as horses, whales, bats, and primates. Birds,[17] fish[18] and perhaps lizards[10] also radiated.
Contents
[hide]Extinction patterns[edit]
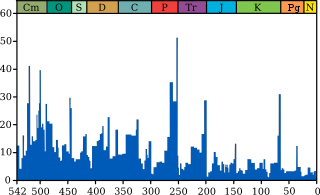
The blue graph shows the apparentpercentage (not the absolute number) of marine animal genera becoming extinct during any given time interval. It does not represent all marine species, just those that are readily fossilized. The labels of the "Big Five" extinction events are clickable hyperlinks; seeExtinction event for more details. (source and image info)
The K–Pg extinction event was severe, global, rapid, and selective. In terms of severity, the event eliminated a vast number of species. Based on marine fossils, it is estimated that 75% or more of all species were wiped out by the K–Pg extinction.[19] In terrestrial ecosystems all animals weighing more than a kilo disappeared.[20]
The event appears to have hit all continents at the same time. Dinosaurs, for example, are known from the Maastrichtian of North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, South America and Antarctica,[21]but are unknown from the Cenozoic anywhere in the world. Similarly, fossil pollen show devastation of the plant communities in areas as far apart as New Mexico, Alaska, China, and New Zealand.[13]
Even though the boundary event was severe, there was significant variability in the rate of extinction between and within different clades. Species that depended on photosynthesis declined or became extinct as atmospheric particles blocked sunlight and reduced the solar energy reaching the Earth's surface. This plant extinction caused a major reshuffling of the dominant plant groups.[22]Omnivores, insectivores and carrion-eaters survived the extinction event, perhaps because of the increased availability of their food sources. No purely herbivorous or carnivorous mammals seem to have survived. Rather, the surviving mammals and birds fed on insects, worms, and snails, which in turn fed on dead plant and animal matter. Scientists hypothesize that these organisms survived the collapse of plant-based food chains because they fed on detritus (non-living organic material).[23][24][25]
In stream communities few animal groups became extinct because stream communities rely less directly on food from living plants and more on detritus that washes in from land, buffering them from extinction.[26] Similar, but more complex patterns have been found in the oceans. Extinction was more severe among animals living in the water column than among animals living on or in the sea floor. Animals in the water column are almost entirely dependent on primary production from living phytoplankton while animals living on or in the ocean floor feed on detritus or can switch to detritus feeding.[23] Coccolithophorids and molluscs (including ammonites, rudists, freshwater snails and mussels), and those organisms whose food chain included these shell builders, became extinct or suffered heavy losses. For example, it is thought that ammonites were the principal food of mosasaurs, a group of giant marine reptiles that became extinct at the boundary.[27] The largest air-breathing survivors of the event, crocodyliforms and champsosaurs, were semi-aquatic and had access to detritus. Modern crocodilians can live as scavengers and can survive for months without food, and their young are small, grow slowly, and feed largely on invertebrates and dead organisms or fragments of organisms for their first few years. These characteristics have been linked to crocodilian survival at the end of the Cretaceous.[24]
After the K–Pg extinction event, biodiversity required substantial time to recover, despite the existence of abundant vacant ecological niches.[23]
Microbiota[edit]
The K–Pg boundary represents one of the most dramatic turnovers in the fossil record for various calcareous nanoplankton that formed the calcium deposits that gave the Cretaceous its name. The turnover in this group is clearly marked at the species level.[28][29] Statistical analysis of marine losses at this time suggests that the decrease in diversity was caused more by a sharp increase in extinctions than by a decrease in speciation.[30] The K–Pg boundary record of dinoflagellatesis not as well-understood, mainly because only microbial cysts provide a fossil record, and not all dinoflagellate species have cyst-forming stages, thereby likely causing diversity to be underestimated.[23] Recent studies indicate that there were no major shifts in dinoflagellates through the boundary layer.[31]
Radiolaria have left a geological record since at least the Ordovician times, and their mineral fossil skeletons can be tracked across the K–Pg boundary. There is no evidence of mass extinction of these organisms, and there is support for high productivity of these species in southern high latitudes as a result of cooling temperatures in the early Paleocene.[23] Approximately 46% of diatom species survived the transition from the Cretaceous to the Upper Paleocene. This suggests a significant turnover in species, but not a catastrophic extinction of diatoms, across the K–Pg boundary.[23][32]
The occurrence of planktonic foraminifera across the K–Pg boundary has been studied since the 1930s.[33] Research spurred by the possibility of an impact event at the K–Pg boundary resulted in numerous publications detailing planktonic foraminiferal extinction at the boundary.[23] However, there is debate ongoing between groups that believe the evidence indicates substantial extinction of these species at the K–Pg boundary,[34] and those who believe the evidence supports multiple extinctions and expansions through the boundary.[35][36]
Numerous species of benthic foraminifera became extinct during the K–Pg extinction event, presumably because they depend on organic debris for nutrients, since the biomass in the ocean is thought to have decreased. However, as the marine microbiota recovered, it is thought that increased speciation of benthic foraminifera resulted from the increase in food sources.[23] Phytoplankton recovery in the early Paleocene provided the food source to support large benthic foraminiferal assemblages, which are mainly detritus-feeding. Ultimate recovery of the benthic populations occurred over several stages lasting several hundred thousand years into the early Paleocene.[37][38]
Marine invertebrates[edit]
There is variability in the fossil record as to the extinction rate of marine invertebrates across the K–Pg boundary. The apparent rate is influenced by the lack of fossil records rather than actual extinction.[23]
Ostracods, a class of small crustaceans that were prevalent in the upper Maastrichtian, left fossil deposits in a variety of locations. A review of these fossils shows that ostracode diversity was lower in the Paleocene than any other time in the Cenozoic. However, current research cannot ascertain whether the extinctions occurred prior to or during the boundary interval itself.[39][40]
Approximately 60% of late-Cretaceous Scleractinia coral genera failed to cross the K–Pg boundary into the Paleocene. Further analysis of the coral extinctions shows that approximately 98% of colonial species, ones that inhabit warm, shallow tropical waters, became extinct. The solitary corals, which generally do not form reefs and inhabit colder and deeper (below the photic zone) areas of the ocean were less impacted by the K–Pg boundary. Colonial coral species rely upon symbiosis with photosynthetic algae, which collapsed due to the events surrounding the K–Pg boundary.[41][42] However, the use of data from coral fossils to support K–Pg extinction and subsequent Paleocene recovery must be weighed against the changes that occurred in coral ecosystems through the K–Pg boundary.[23]
The numbers of cephalopod, echinoderm, and bivalve genera exhibited significant diminution after the K–Pg boundary.[23] Most species of brachiopods, a small phylum of marine invertebrates, survived the K–Pg extinction event and diversified during the early Paleocene.
Except for nautiloids (represented by the modern order Nautilida) and coleoids (which had already diverged into modern octopodes, squids, and cuttlefish) all other species of the molluscan class Cephalopoda became extinct at the K–Pg boundary. These included the ecologically significant belemnoids, as well as the ammonoids, a group of highly diverse, numerous, and widely distributed shelled cephalopods. Researchers have pointed out that the reproductive strategy of the surviving nautiloids, which rely upon few and larger eggs, played a role in outsurviving their ammonoid counterparts through the extinction event. The ammonoids utilized a planktonic strategy of reproduction (numerous eggs and planktonic larvae), which would have been devastated by the K–Pg extinction event. Additional research has shown that subsequent to this elimination of ammonoids from the global biota, nautiloids began an evolutionary radiation into shell shapes and complexities theretofore known only from ammonoids.[43][44]
Approximately 35% of echinoderm genera became extinct at the K–Pg boundary, although taxa that thrived in low-latitude, shallow-water environments during late Cretaceous had the highest extinction rate. Mid-latitude, deep-water echinoderms were much less affected at the K–Pg boundary. The pattern of extinction points to habitat loss, specifically the drowning of carbonate platforms, the shallow-water reefs in existence at that time, by the extinction event.[45]
Other invertebrate groups, including rudists (reef-building clams) and inoceramids (giant relatives of modern scallops), also became extinct at the K–Pg boundary.[46][47]
Fish[edit]
There are substantial fossil records of jawed fishes across the K–Pg boundary, which provides good evidence of extinction patterns of these classes of marine vertebrates. Within cartilaginous fish, approximately 80% of the sharks, rays, andskates families survived the extinction event,[23] and more than 90% of teleost fish (bony fish) families survived.[48] There is evidence of a mass kill of bony fishes at a fossil site immediately above the K–Pg boundary layer on Seymour Islandnear Antarctica, apparently precipitated by the K–Pg extinction event.[49] However, the marine and freshwater environments of fishes mitigated environmental effects of the extinction event.[50]
Terrestrial invertebrates[edit]
Insect damage to the fossilized leaves of flowering plants from fourteen sites in North America were used as a proxy for insect diversity across the K–Pg boundary and analyzed to determine the rate of extinction. Researchers found that Cretaceous sites, prior to the extinction event, had rich plant and insect-feeding diversity. However, during the early Paleocene, flora were relatively diverse with little predation from insects, even 1.7 million years after the extinction event.[51][52]
Terrestrial plants[edit]
There is overwhelming evidence of global disruption of plant communities at the K–Pg boundary.[13][13][53][54] Extinctions are seen both in studies of fossil pollen, and fossil leaves.[13] In North America, the data suggest massive devastation and mass extinction of plants at the K–Pg boundary sections, although there were substantial megafloral changes before the boundary.[13][55] In North America, approximately 57% of plant species became extinct. In high southern hemisphere latitudes, such as New Zealand and Antarctica the mass die-off of flora caused no significant turnover in species, but dramatic and short-term changes in the relative abundance of plant groups.[51][56] In some regions, Paleocene recovery of plants began with recolonizations by fern species, represented as a fern spike in the geologic record; this same pattern of fern recolonization was observed after the 1980 Mount St. Helens eruption.[57] However the patterns of recovery were quite variable. Different fern species were responsible for the fern spike in different areas, and in some regions, no fern spike is evident.[citation needed]
Due to the wholesale destruction of plants at the K–Pg boundary there was a proliferation of saprotrophic organisms such as fungi that do not require photosynthesis and use nutrients from decaying vegetation. The dominance of fungal species lasted only a few years while the atmosphere cleared and there was plenty of organic matter to feed on. Once the atmosphere cleared, photosynthetic organisms like ferns and other plants returned.[58] Polyploidy appears to have enhanced the ability of flowering plants to survive the extinction, probably because the additional copies of the genome such plants possessed allowed them to more readily adapt to the rapidly changing environmental conditions that followed the impact.[59]
Amphibians[edit]
There is limited evidence for extinction of amphibians at the K–Pg boundary. A study of fossil vertebrates across the K–Pg boundary in Montana concluded that no species of amphibian became extinct.[60] Yet there are several species of Maastrichtian amphibian, not included as part of this study, which are unknown from the Paleocene. These include the frog Theatonius lancensis [61] and the albanerpetontid Albanerpeton galaktion;[62] therefore some amphibians do seem to have become extinct at the boundary. The relatively low levels of extinction seen among amphibians probably reflect the low extinction rates seen in freshwater animals.[63]
Non-archosaur reptiles[edit]
The two living non-archosaurian reptile taxa, testudines (turtles) and lepidosaurs (snakes, lizards, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards)), along with choristoderes (semi-aquatic archosauromorphs that died out in the early Miocene), survived through the K–Pg boundary.[23] Over 80% of Cretaceous turtle species passed through the K–Pg boundary. Additionally, all six turtle families in existence at the end of the Cretaceous survived into the Paleogene and are represented by current species.[64] Living lepidosaurs include Rhynchocephalia (tuataras) and Squamata. The Rhynchocephalia were a widespread and relatively successful group of lepidosaurs in the early Mesozoic, but began to decline by the mid-Cretaceous. They are represented today by a single genus located exclusively in New Zealand.[65]
The order Squamata, which is represented today by lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians, radiated into various ecological niches during the Jurassic and were successful throughout the Cretaceous. They survived through the K–Pg boundary and are currently the most successful and diverse group of living reptiles with more than 6,000 extant species. No known family of terrestrial squamates became extinct at the boundary, and fossil evidence indicates they did not suffer any significant decline in numbers. Their small size, adaptable metabolism, and ability to move to more favorable habitats were key factors in their survivability during the late Cretaceous and early Paleocene.[23][64] Giant non-archosaurian aquatic reptiles such as mosasaurs and plesiosaurs, which were the top marine predators of their time, became extinct by the end of the Cretaceous.[66][67]
Archosaurs[edit]
The archosaur clade includes two surviving groups, crocodilians and birds, along with the extinct non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs.[68]
Crocodyliforms[edit]
Ten families of crocodilians or their close relatives are represented in the Maastrichtian fossil records, of which five died out prior to the K–Pg boundary.[69] Five families have both Maastrichtian and Paleocene fossil representatives. All of the surviving families of crocodyliforms inhabited freshwater and terrestrial environments—except for the Dyrosauridae, which lived in freshwater and marine locations. Approximately 50% of crocodyliform representatives survived across the K–Pg boundary, the only apparent trend being that no large crocodiles survived.[23] Crocodyliform survivability across the boundary may have resulted from their aquatic niche and ability to burrow, which reduced susceptibility to negative environmental effects at the boundary.[50] Jouve and colleagues suggested in 2008 that juvenile marine crocodyliforms lived in freshwater environments like modern marine crocodile juveniles, which would have helped them survive where other marine reptiles became extinct; freshwater environments were not as strongly affected by the K–Pg extinction event as marine environments.[70]
The Choristodera, a generally crocodile-like group of uncertain phylogeny (possibly archosaurian) also survived the event, only to go extinct in the Miocene.[71]
Pterosaurs[edit]
One family of pterosaurs, Azhdarchidae, was definitely present in the Maastrichtian, and it became extinct at the K–Pg boundary. These large pterosaurs were the last representatives of a declining group that contained 10 families during the mid-Cretaceous. Smaller pterosaurs became extinct prior to the Maastrichtian during a period that saw a decline in smaller animal species while larger species became more prevalent. Recently, several pterosaur taxa have been discovered dating to the Campanian/Maastrichtian, such as the ornithocheirids Piksi and "Ornithocheirus", possible pteranodontids and nyctosaurids, and a tapejarid.[72] While this was occurring, modern birds were undergoing diversification and replacing archaic birds and pterosaur groups, possibly due to direct competition, or they simply filled empty niches.[50][73][74]
Birds[edit]
Most paleontologists regard birds as the only surviving dinosaurs (see Origin of birds). It was thought that all non-neornithean birds became extinct, including flourishing groups like enantiornithines and hesperornithiforms.[75] More recent research, however, suggests that one or more non-neornithine birds may have survived the extinction event.[76] Several analyses of bird fossils show divergence of species prior to the K–Pg boundary, and that duck, chicken and ratite bird relatives coexisted with non-avian dinosaurs.[77] Large collections of bird fossils representing a range of different species provides definitive evidence for the persistence of archaic birds to within 300,000 years of the K–Pg boundary. None of them are known to survive into the Paleogene, and their persistence into the latest Maastrichtian therefore provides strong evidence for a mass extinction of archaic birds coinciding with the Chicxulub asteroid impact. A small fraction of the Cretaceous bird species survived the impact, giving rise to today's birds.[76][78] So far, only a single bird species, which has not been named, has been confidently identified from both above and below the K–Pg boundary (it is present in the Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation and Danian Fort Union Formation).[76] The only bird group known for certain to have survived the K–Pg boundary is the Neornithines (though one Paleogene species, Qinornis paleocenica, may represent a surviving non-neornithine bird).[76] Neornithines may have been able to survive the extinction as a result of their abilities to dive, swim, or seek shelter in water and marshlands. Many species of neornithines can build burrows, or nest in tree holes or termite nests, all of which provided shelter from the environmental effects at the K–Pg boundary. Long-term survival past the boundary was assured as a result of filling ecological niches left empty by extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.[50]
Non-avian dinosaurs[edit]
Excluding a few controversial claims, scientists agree that all non-avian dinosaurs became extinct at the K–Pg boundary. The dinosaur fossil record has been interpreted to show both a decline in diversity and no decline in diversity during the last few million years of the Cretaceous, and it may be that the quality of the dinosaur fossil record is simply not good enough to permit researchers to distinguish between the options.[79] Since there is no evidence that late Maastrichtian nonavian dinosaurs could burrow, swim or dive, they were unable to shelter themselves from the worst parts of any environmental stress that occurred at the K–Pg boundary. It is possible that small dinosaurs (other than birds) did survive, but they would have been deprived of food as both herbivorous dinosaurs would have found plant material scarce, and carnivores would have quickly found prey in short supply.[50]
The growing consensus about the endothermy of dinosaurs (see dinosaur physiology) helps to understand their full extinction in contrast with their close relatives, the crocodilians. Ectothermic ("cold-blooded") crocodiles have very limited needs for food (they can survive several months without eating) while endothermic ("warm-blooded") animals of similar size need much more food to sustain their faster metabolism. Thus, under the circumstances of food chain disruption previously mentioned, non-avian dinosaurs died,[22] while some crocodiles survived. In this context, the survival of other endothermic animals, such as some birds and mammals, could be due, among other reasons, to their smaller needs for food, related to their small size at the extinction epoch.[80]
Whether the extinction occurred gradually or suddenly has been debated, as both views have support from the fossil record. A study of 29 fossil sites in Catalan Pyrenees of Europe in 2010 supports the view that dinosaurs there had great diversity until the asteroid impact, with over 100 living species.[81] However, more recent research indicates that this figure is obscured by taphonomical biases and the sparsity of the continental fossil record. The results of this study, which were based on estimated real global biodiversity, showed that between 628 and 1078 non-avian dinosaur species were alive at the end of the Cretaceous and underwent sudden extinction after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.[82]Alternatively, interpretation based on the fossil-bearing rocks along the Red Deer River in Alberta, Canada, supports the gradual extinction of non-avian dinosaurs; during the last 10 million years of the Cretaceous layers there, the number of dinosaur species seems to have decreased from about 45 to about 12. Other scientists have pointed out the same.[83]
Several researchers support the existence of Paleocene dinosaurs. Evidence of this existence is based on the discovery of dinosaur remains in the Hell Creek Formation up to 1.3 m (4.3 ft) above and 40,000 years later than the K–Pg boundary.[84] Pollen samples recovered near a fossilized hadrosaur femur recovered in the Ojo Alamo Sandstone at the San Juan River indicate that the animal lived during the Cenozoic, approximately 64.5 Ma (about 1 million years after the K–Pg extinction event). If their existence past the K–Pg boundary can be confirmed, these hadrosaurids would be considered a dead clade walking.[85] Scientific consensus is that these fossils were eroded from their original locations and then re-buried in much later sediments (also known as reworked fossils).[86]
Mammals[edit]
All major Cretaceous mammalian lineages, including monotremes (egg-laying mammals), multituberculates, marsupials and placentals, dryolestoideans,[87] and gondwanatheres[88] survived the K–Pg extinction event, although they suffered losses. In particular, marsupials largely disappeared from North America, and the Asian deltatheroidans, primitive relatives of extant marsupials, became extinct.[89] In the Hell Creek beds of North America, at least half of the ten known multituberculate species and all eleven marsupial species are not found above the boundary.[79]
Mammalian species began diversifying approximately 30 million years prior to the K–Pg boundary. Diversification of mammals stalled across the boundary.[90] Current research indicates that mammals did not explosively diversify across the K–Pg boundary, despite the environment niches made available by the extinction of dinosaurs.[91] Several mammalian orders have been interpreted as diversifying immediately after the K–Pg boundary, including Chiroptera (bats) and Cetartiodactyla (a diverse group that today includes whales and dolphins and even-toed ungulates),[91] although recent research concludes that onlymarsupial orders diversified after the K–Pg boundary.[90]
K–Pg boundary mammalian species were generally small, comparable in size to rats; this small size would have helped them to find shelter in protected environments. In addition, it is postulated that some early monotremes, marsupials, and placentals were semiaquatic or burrowing, as there are multiple mammalian lineages with such habits today. Any burrowing or semiaquatic mammal would have had additional protection from K–Pg boundary environmental stresses.[50]
Evidence[edit]
North American fossils[edit]
In North American terrestrial sequences, the extinction event is best represented by the marked discrepancy between the rich and relatively abundant late-Maastrichtian palynomorph record and the post-boundary fern spike.[53]
At present the most informative sequence of dinosaur-bearing rocks in the world from the K–Pg boundary is found in western North America, particularly the late Maastrichtian-age Hell Creek Formation of Montana, US. This formation, when compared with the older (approximately 75 Ma) Judith River/Dinosaur Park Formations (from Montana, USA, and Alberta, Canada, respectively) provides information on the changes in dinosaur populations over the last 10 million years of the Cretaceous. These fossil beds are geographically limited, covering only part of one continent.[79]
The middle–late Campanian formations show a greater diversity of dinosaurs than any other single group of rocks. The late Maastrichtian rocks contain the largest members of several major clades: Tyrannosaurus, Ankylosaurus,Pachycephalosaurus, Triceratops and Torosaurus,[92] which suggests food was plentiful immediately prior to the extinction.
In addition to rich dinosaur fossils, there are also plant fossils that illustrate the reduction in plant species across the K–Pg boundary. In the sediments below the K–Pg boundary the dominant plant remains are angiosperm pollen grains, but the actual boundary layer contains little pollen and is dominated by fern spores.[93] More usual pollen levels gradually resume above the boundary layer. This is reminiscent of areas blighted by modern volcanic eruptions, where the recovery is led by ferns, which are later replaced by larger angiosperm plants.[94]
Marine fossils[edit]
The mass extinction of marine plankton appears to have been abrupt and right at the K–Pg boundary.[95] Ammonite genera became extinct at or near the K–Pg boundary; however, there was a smaller and slower extinction of ammonite genera prior to the boundary that was associated with a late Cretaceous marine regression. The gradual extinction of most inoceramid bivalves began well before the K–Pg boundary, and a small, gradual reduction in ammonite diversity occurred throughout the very late Cretaceous.[96] Further analysis shows that several processes were in progress in the late Cretaceous seas and partially overlapped in time, then ended with the abrupt mass extinction.[96]
Megatsunamis[edit]
The scientific consensus is that bolide impact at the K–Pg boundary left tsunami deposits and sediments around the area of the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico.[97] These deposits have been identified in the La Popa basin in northeasternMexico,[98] platform carbonates in northeastern Brazil,[99] and Atlantic deep-sea sediments.[100]
Duration[edit]
The length of time taken for the extinction to occur is a controversial issue, because some theories about the extinction's causes require a rapid extinction over a relatively short period (from a few years to a few thousand years) while others require longer periods. The issue is difficult to resolve because of the Signor–Lipps effect; that is, the fossil record is so incomplete that most extinct species probably died out long after the most recent fossil that has been found.[101] Scientists have also found very few continuous beds of fossil-bearing rock which cover a time range from several million years before the K–Pg extinction to a few million years after it.[23]
Chicxulub asteroid impact[edit]
Evidence for impact[edit]
In 1980, a team of researchers consisting of Nobel prize-winning physicist Luis Alvarez, his son geologist Walter Alvarez, and chemists Frank Asaro and Helen Michel discovered that sedimentary layers found all over the world at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary contain a concentration of iridium many times greater than normal (30, 160 and 20 times in three sections originally studied). Iridium is extremely rare in Earth's crust because it is a siderophile element, and therefore most of it travelled with the iron as it sank into Earth's core during planetary differentiation. As iridium remains abundant in most asteroids andcomets, the Alvarez team suggested that an asteroid struck the Earth at the time of the K–Pg boundary.[4] There were earlier speculations on the possibility of an impact event, but this was the first hard evidence of an impact.[102]
This hypothesis was viewed as radical when first proposed, but additional evidence soon emerged. The boundary clay was found to be full of minute spherules of rock, crystallized from droplets of molten rock formed by the impact.[103] Shocked quartz and other minerals were also identified in the K–Pg boundary.[104][105] Shocked minerals have their internal structure deformed, and are created by intense pressures such as those associated with nuclear blasts or meteorite impacts. The identification of giant tsunami beds along the Gulf Coast and the Caribbean also provided evidence for impact,[106] and suggested that the impact may have occurred nearby—as did the discovery that the K–Pg boundary became thicker in the southern United States, with meter-thick beds of debris occurring in northern New Mexico.[13]
K/T impact site on a contemporary world map (65 mya)[107]
Further research identified the giant Chicxulub crater, buried under Chicxulub on the coast of Yucatán, Mexico as the source of the K–Pg boundary clay. Identified in 1990[6] based on work by geophysicist Glen Penfield in 1978, the crater is oval, with an average diameter of roughly 180 kilometres (110 mi), about the size calculated by the Alvarez team.[108] The discovery of the crater – a necessary prediction of the impact hypothesis – provided conclusive evidence for a K–Pg impact, and strengthened the hypothesis that the extinction was caused by an impact.
In 2007, a hypothesis was put forth that argued the impactor that killed the dinosaurs belonged to the Baptistina family of asteroids.[109] Concerns have been raised regarding the reputed link, in part because very few solid observational constraints exist of the asteroid or family.[110] Indeed, it was recently discovered that 298 Baptistina does not share the same chemical signature as the source of the K–Pg impact.[111] Although this finding may make the link between the Baptistina family and K–Pg impactor more difficult to substantiate, it does not preclude the possibility.[111] A 2011 WISE study of reflected light from the asteroids of the family estimated the break-up at 80 Ma, giving it insufficient time to shift orbits and impact the Earth by 66 Ma.[112]
In a 2013 paper, Paul Renne of the Berkeley Geochronology Center reported that the date of the asteroid event is 66.043±0.011 million years ago, based on argon–argon dating. He further posits that the mass extinction occurred within 33,000 years of this date.[2][113]
Effects of impact[edit]
Such an impact would have inhibited photosynthesis by creating a dust cloud that blocked sunlight for up to a year, and by injecting sulfuric acid aerosols into the stratosphere, which might have reduced sunlight reaching the Earth's surface by 10–20%. It has been argued that it would take at least ten years for such aerosols to dissipate, which would account for the extinction of plants andphytoplankton, and of organisms dependent on them (including predatory animals as well as herbivores). Small creatures whose food chains were based on detritus would have a reasonable chance of survival.[80][95] The consequences of reentry of ejecta into Earth's atmosphere would include a brief (hours long) but intense pulse of infrared radiation, killing exposed organisms.[50] Global firestormslikely resulted from the heat pulse and the fall back to Earth of incendiary fragments from the blast. Recent research indicates that the global debris layer deposited by the impact contained enough soot to suggest that the entire terrestrial biosphere had burned.[114] The high O
2 levels during the late Cretaceous would have supported intense combustion. The level of atmospheric O
2 plummeted in the early Cenozoic era. If widespread fires occurred, they would have increased the CO
2 content of the atmosphere and caused a temporary greenhouse effect once the dust cloud settled, and this would have exterminated the most vulnerable organisms that survived the period immediately after the impact.[115]
2 levels during the late Cretaceous would have supported intense combustion. The level of atmospheric O
2 plummeted in the early Cenozoic era. If widespread fires occurred, they would have increased the CO
2 content of the atmosphere and caused a temporary greenhouse effect once the dust cloud settled, and this would have exterminated the most vulnerable organisms that survived the period immediately after the impact.[115]
The impact may also have produced acid rain, depending on what type of rock the asteroid struck. However, recent research suggests this effect was relatively minor, lasting for approximately12 years.[95] The acidity was neutralized by the environment, and the survival of animals vulnerable to acid rain effects (such as frogs) indicate this was not a major contributor to extinction. Impact theories can only explain very rapid extinctions, since the dust clouds and possible sulfuric aerosols would wash out of the atmosphere in a fairly short time—possibly within 10 years.[116]
The shape and location of the crater indicate further causes of devastation in addition to the dust cloud. The asteroid landed in the ocean and would have caused megatsunamis, for which evidence has been found in several locations in the Caribbean and eastern United States—marine sand in locations that were then inland, and vegetation debris and terrestrial rocks in marine sediments dated to the time of the impact. The asteroid landed in a bed of gypsum (calcium sulfate), which would have produced a vast sulfur dioxide aerosol. This would have further reduced the sunlight reaching the Earth's surface and then precipitated as acid rain, killing vegetation, plankton, and organisms that build shells from calcium carbonate (coccolithophores and molluscs). In February 2008, a team of researchers used seismic images of the crater to determine that the impactor landed in deeper water than was previously assumed. They argued that this would have resulted in increased sulfate aerosols in the atmosphere, which could have made the impact deadlier by altering climate and by generating acid rain.[117]
Most paleontologists now agree that an asteroid did hit the Earth at approximately the end of the Cretaceous, but there is an ongoing dispute whether the impact was the sole cause of the extinctions.[36][118]There is evidence that there was an interval of about 300 ka from the impact to the mass extinction.[119] In 1997, paleontologist Sankar Chatterjee drew attention to the proposed and much larger 600 km (370 mi) Shiva crater and the possibility of a multiple-impact scenario.
In March 2010 an international panel of scientists endorsed the asteroid hypothesis, specifically the Chicxulub impact, as being the cause of the extinction. A team of 41 scientists reviewed 20 years of scientific literature and in so doing also ruled out other theories such as massive volcanism. They had determined that a 10-to-15-kilometre (6.2 to 9.3 mi) space rock hurtled into Earth at Chicxulub on Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. The collision would have released the same energy as 100 teratonnes of TNT (420 ZJ), over a billion times the energy of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.[7]
Alternative hypotheses[edit]
The fact that the extinctions occur at the same time as the Chicxulub asteroid impact strongly supports the impact hypothesis of extinction. However, some scientists continue to dispute the role of the Chicxulub impact in driving the extinction, and to suggest that other events may have contributed to the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. In particular, volcanic eruptions, climate change, sea level change, and other impact events have been suggested to play a role in driving the K–Pg extinction.
Deccan Traps[edit]
Main article: Deccan Traps
Before 2000, arguments that the Deccan Traps flood basalts caused the extinction were usually linked to the view that the extinction was gradual, as the flood basalt events were thought to have started around 68 Mya and lasted more than2 million years. The most recent evidence shows that the traps erupted over a period of 800,000 years spanning the K–Pg boundary, and therefore may be responsible for the extinction and the delayed biotic recovery thereafter.[120]
The Deccan Traps could have caused extinction through several mechanisms, including the release of dust and sulfuric aerosols into the air, which might have blocked sunlight and thereby reduced photosynthesis in plants. In addition, Deccan Trap volcanism might have resulted in carbon dioxide emissions that increased the greenhouse effect when the dust and aerosols cleared from the atmosphere.[121]
In the years when the Deccan Traps hypothesis was linked to a slower extinction, Luis Alvarez (who died in 1988) replied that paleontologists were being misled by sparse data. While his assertion was not initially well-received, later intensive field studies of fossil beds lent weight to his claim. Eventually, most paleontologists began to accept the idea that the mass extinctions at the end of the Cretaceous were largely or at least partly due to a massive Earth impact. However, even Walter Alvarez has acknowledged that there were other major changes on Earth even before the impact, such as a drop in sea level and massive volcanic eruptions that produced the Indian Deccan Traps, and these may have contributed to the extinctions.[122]
Multiple impact event[edit]
Several other craters also appear to have been formed about the time of the K–Pg boundary. This suggests the possibility of near simultaneous multiple impacts, perhaps from a fragmented asteroidal object, similar to the Shoemaker–Levy 9impact with Jupiter. In addition to the 180 km (110 mi) Chicxulub Crater, there is the 24 km (15 mi) Boltysh crater in Ukraine (65.17±0.64 Ma), the 20 km (12 mi) Silverpit crater, a suspected impact crater in the North Sea (62.5±2.5 Ma), and the controversial and much larger 600 km (370 mi) Shiva crater. Any other craters that might have formed in the Tethys Ocean would have been obscured by tectonic events like the relentless northward drift of Africa and India.[123][124][125][126]
Maastrichtian sea-level regression[edit]
There is clear evidence that sea levels fell in the final stage of the Cretaceous by more than at any other time in the Mesozoic era. In some Maastrichtian stage rock layers from various parts of the world, the later layers are terrestrial; earlier layers represent shorelines and the earliest layers represent seabeds. These layers do not show the tilting and distortion associated with mountain building, therefore, the likeliest explanation is a "regression", that is, a drop in sea level. There is no direct evidence for the cause of the regression, but the explanation currently accepted as most likely is that the mid-ocean ridges became less active and therefore sank under their own weight.[23][127]
A severe regression would have greatly reduced the continental shelf area, which is the most species-rich part of the sea, and therefore could have been enough to cause a marine mass extinction. However research concludes that this change would have been insufficient to cause the observed level of ammonite extinction. The regression would also have caused climate changes, partly by disrupting winds and ocean currents and partly by reducing the Earth's albedo and therefore increasing global temperatures.[96]
Marine regression also resulted in the loss of epeiric seas, such as the Western Interior Seaway of North America. The loss of these seas greatly altered habitats, removing coastal plains that ten million years before had been host to diverse communities such as are found in rocks of the Dinosaur Park Formation. Another consequence was an expansion of freshwater environments, since continental runoff now had longer distances to travel before reaching oceans. While this change was favorable to freshwater vertebrates, those that prefer marine environments, such as sharks, suffered.[79]
Multiple causes[edit]
In a review article, J. David Archibald and David E. Fastovsky discussed a scenario combining three major postulated causes: volcanism, marine regression, and extraterrestrial impact. In this scenario, terrestrial and marine communities were stressed by the changes in and loss of habitats. Dinosaurs, as the largest vertebrates, were the first affected by environmental changes, and their diversity declined. At the same time, particulate materials from volcanism cooled and dried areas of the globe. Then, an impact event occurred, causing collapses in photosynthesis-based food chains, both in the already-stressed terrestrial food chains and in the marine food chains. The major difference between this hypothesis and the single-cause hypotheses is that its proponents view the suggested single causes as either not sufficient in strength to cause the extinctions or not likely to produce the taxonomic pattern of the extinction.[79]
Recovery and radiation[edit]
The K–Pg extinction had a profound effect on the evolution of life on earth. The elimination of dominant Cretaceous groups allowed other organisms to take their place, spurring a remarkable series of adaptive radiations in the Paleogene.[16]The most striking example is the replacement of dinosaurs by mammals. After the K–Pg extinction, mammals evolved rapidly to fill the niches left vacant by the dinosaurs. Within mammalian genera, new species were approximately 9.1% larger after the K–Pg boundary.[128]
Other groups also underwent major radiations. Based on molecular sequencing and fossil dating, Neoaves appeared to radiate after the K–Pg boundary.[17][129] They even produced giant, flightless forms, such as the herbivorous Gastornis andDromornithidae, and the predatory Phorusrhacidae. The extinction of Cretaceous lizards and snakes may have led to the radiation of modern groups such as iguanas, monitor lizards, and boas.[10] On land, giant boid and enormous madtsoiidsnakes appeared, and in the seas, giant sea snakes radiated. Teleost fish diversified explosively,[18] filling the niches left vacant by the extinction. Groups appearing in the Paleocene and Eocene include billfish, tunas, eels, and flatfish. Major changes are also seen in Paleogene insect communities. Many groups of ants were present in the Cretaceous, but in the Eocene ants became dominant and diverse, with larger colonies. Butterflies diversified as well, perhaps to take the place of leaf-eating insects wiped out by the extinction. The advanced mound-building termites, Termitidae, also appear to have risen in importance.[130]
See also[edit]
- Climate across Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary
- Late Devonian extinction
- Ordovician–Silurian extinction events
- Permian–Triassic extinction event
- Triassic–Jurassic extinction event
References and notes[edit]
- ^ The abbreviation is derived from the juxtaposition of K, the common abbreviation for the Cretaceous, which in turn originates from the correspondent German term Kreide, and Pg, which is the abbreviation for the Paleogene.
- ^ The former designation includes the term 'Tertiary' (abbreviated as T), which is now discouraged as a formal geochronological unit by the International Commission on Stratigraphy.[1]
- ^ Ogg, James G.; Gradstein, F. M; Gradstein, Felix M. (2004). A geologic time scale 2004. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-78142-6.
- ^ a b Renne, Paul R.; Deino, Alan L.; Hilgen, Frederik J.; Kuiper, Klaudia F.; Mark, Darren F.; Mitchell III, William S.; Morgan, Leah E.; Mundil, Roland; Smit, Jan; Hilgen, Frederik J.; Kuiper, Klaudia F.; Mark, Darren F.; Mitchell, William S.; Morgan, Leah E.; Mundil, Roland; Smit, Jan (7 February 2013). "Time Scales of Critical Events Around the Cretaceous-Paleogene Boundary". Science 339(6120): 684–687. Bibcode:2013Sci...339..684R.doi:10.1126/science.1230492. PMID 23393261.
- ^ Fortey, R (1999). Life: A Natural History of the First Four Billion Years of Life on Earth. Vintage. pp. 238–260. ISBN 978-0-375-70261-7.
- ^ a b Alvarez LW, Alvarez W, Asaro F, Michel HV (1980). "Extraterrestrial cause for the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction". Science 208 (4448): 1095–1108.Bibcode:1980Sci...208.1095A. doi:10.1126/science.208.4448.1095.PMID 17783054.
- ^ Vellekoop J, Sluijs A, Smit J et al. (May 2014). "Rapid short-term cooling following the Chicxulub impact at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111 (21): 7537–41. doi:10.1073/pnas.1319253111.PMID 24821785.
- ^ a b Hildebrand, A. R., G. T. Penfield, et al. (1991). "Chicxulub crater: a possible Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary impact crater on the Yucatán peninsula, Mexico." Geology 19: 867-871.
- ^ a b c Schulte, P. et al. (5 March 2010). "The Chicxulub Asteroid Impact and Mass Extinction at the Cretaceous-Paleogene Boundary". Science 327 (5970): 1214–1218. Bibcode:2010Sci...327.1214S. doi:10.1126/science.1177265.PMID 20203042.
- ^ Keller G (2012). "The Cretaceous–Tertiary Mass Extinction, Chicxulub Impact, and Deccan Volcanism. Earth and Life". In Talent JA. Earth and Life: Global Biodiversity, Extinction Intervals and Biogeographic Perturbations Through Time. Springer. pp. 759–793. ISBN 978-9048134274.
- ^ Longrich N. R., Tokaryk T. T. et al. (2011). "Mass extinction of birds at the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108 (37): 15253–15257. Bibcode:2011PNAS..10815253L.doi:10.1073/pnas.1110395108.
- ^ a b c Longrich NR, Bhullar BA, Gauthier JA; Bhullar; Gauthier (December 2012). "Mass extinction of lizards and snakes at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 (52): 21396–401.doi:10.1073/pnas.1211526110. PMC 3535637. PMID 23236177.
- ^ Labandeira CC, Johnson KR et al. (2002). "Preliminary assessment of insect herbivory across the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary: major extinction and minimum rebound". In Hartman JH, Johnson KR, Nichols DJ. The Hell Creek Formation and the Cretaceous-Tertiary Boundary in the Northern Great Plains: An Integrated Continental Record of the End of the Cretaceous. Geological Society of America. pp. 297–327. ISBN 978-0813723617.
- ^ Rehan, Sandra M.; Leys, Remko; Schwarz, Michael P. (2013). "First Evidence for a Massive Extinction Event Affecting Bees Close to the K-T Boundary".PLoS ONE 8 (10): e76683. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076683. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3806776. PMID 24194843.
- ^ a b c d e f g Nichols, D. J. and K. R. Johnson (2008). Plants and the K–T Boundary. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Friedman M (2009). "Ecomorphological selectivity among marine teleost fishes during the end-Cretaceous extinction". PNAS 106 (13): 5218–5223.doi:10.1073/pnas.0808468106. PMC 2664034. PMID 19276106.
- ^ Jablonski, D., 1994. Extinctions in the fossil record (and discussion). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B. 344, 11-17.
- ^ a b Alroy J (1999). "The fossil record of North American Mammals: evidence for a Palaeocene evolutionary radiation". Systematic Biology 48 (1): 107–118.doi:10.1080/106351599260472. PMID 12078635.
- ^ a b Feduccia A (1995). "Explosive evolution in Tertiary birds and mammals".Science 267 (5198): 637–638. doi:10.1126/science.267.5198.637.PMID 17745839.
- ^ a b Friedman M (2010). "Explosive morphological diversification of spiny-finned teleost fishes in the aftermath of the end-Cretaceous extinction".Proceedings of the Royal Society B 277 (1688): 1675–1683.doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.2177. PMC 2871855. PMID 20133356.
- ^ Jablonski, D.; Chaloner, W. G. (1994). "Extinctions in the fossil record (and discussion)". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B 344 (1307): 11–17. doi:10.1098/rstb.1994.0045.
- ^ Baby Boom: Did Retained Juvenile Traits Help Birds Outlive Dinosaurs?
- ^ Weishampel, D. B., P. M. Barrett (2004). "Dinosaur Distribution". In David B Weishampel; Peter Dodson; Halszka Osmólska. The Dinosauria (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 517–606. OCLC 441742117.
- ^ a b Wilf P, Johnson KR; Johnson (2004). "Land plant extinction at the end of the Cretaceous: a quantitative analysis of the North Dakota megafloral record".Paleobiology 30 (3): 347–368. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2004)030<0347:LPEATE>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0094-8373.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q MacLeod N; Rawson PF; Forey PL; Banner FT; Boudagher-Fadel MK; Bown PR; Burnett JA; Chambers P; Culver S; Evans SE; Jeffery C; Kaminski MA; Lord AR; Milner AC; Milner AR; Morris N; Owen E; Rosen BR; Smith AB; Taylor PD; Urquhart E; Young JR (1997). "The Cretaceous–Tertiary biotic transition". Journal of the Geological Society 154(2): 265–292. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.154.2.0265.
- ^ a b Sheehan Peter M, Hansen Thor A; Hansen (1986). "Detritus feeding as a buffer to extinction at the end of the Cretaceous". Geology 14 (10): 868–870.Bibcode:1986Geo....14..868S. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1986)14<868:DFAABT>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613. Retrieved2007-07-04.
- ^ Aberhan M, Weidemeyer S, Kieesling W, Scasso RA, Medina FA; Weidemeyer; Kiessling; Scasso; Medina (2007). "Faunal evidence for reduced productivity and uncoordinated recovery in Southern Hemisphere Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary sections". Geology 35 (3): 227–230. Bibcode:2007Geo....35..227A.doi:10.1130/G23197A.1.
- ^ Sheehan Peter M, Fastovsky DE; Fastovsky (1992). "Major extinctions of land-dwelling vertebrates at the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary, eastern Montana".Geology 20 (6): 556–560. Bibcode:1992Geo....20..556S. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0556:MEOLDV>2.3.CO;2. Retrieved 2007-06-22.
- ^ Kauffman E (2004). "Mosasaur Predation on Upper Cretaceous Nautiloids and Ammonites from the United States Pacific Coast". PALAIOS (Society for Sedimentary Geology) 19 (1): 96–100. doi:10.1669/0883-1351(2004)019<0096:MPOUCN>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0883-1351. Retrieved2007-06-17.
- ^ Pospichal JJ (1996). "Calcareous nannofossils and clastic sediments at the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary, northeastern Mexico". Geology 24 (3): 255–258. Bibcode:1996Geo....24..255P. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0255:CNACSA>2.3.CO;2.
- ^ Bown P (2005). "Selective calcareous nannoplankton survivorship at the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary". Geology 33 (8): 653–656.Bibcode:2005Geo....33..653B. doi:10.1130/G21566.1.
- ^ Bambach RK, Knoll AH, Wang SC; Knoll; Wang (2004). "Origination, extinction, and mass depletions of marine diversity". Paleobiology 30 (4): 522–542. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2004)030<0522:OEAMDO>2.0.CO;2.ISSN 0094-8373.
- ^ Gedl P (2004). "Dinoflagellate cyst record of the deep-sea Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary at Uzgru, Carpathian Mountains, Czech Republic". Geological Society, London, Special Publications 230: 257–273.Bibcode:2004GSLSP.230..257G. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.230.01.13.
- ^ MacLeod N (1998). "Impacts and marine invertebrate extinctions".Geological Society, London, Special Publications 140 (1): 217–246.Bibcode:1998GSLSP.140..217M. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.140.01.16.
- ^ Courtillot, V (1999). Evolutionary Catastrophes: The Science of Mass Extinction. Cambridge University Press. p. 2. ISBN 0-521-58392-6.
- ^ Arenillas I, Arz JA, Molina E and Dupuis C (2000). "An independent test of planktic foraminiferal turnover across the Cretaceous/Paleogene (K/P) boundary at El Kef, Tunisia: catastrophic mass extinction and possible survivorship".Micropaleontology 46 (1): 31–49. JSTOR 1486024.
- ^ MacLeod, N (1996). Nature of the Cretaceous-Tertiary (K–T) planktonic foraminiferal record: stratigraphic confidence intervals, Signor–Lipps effect, and patterns of survivorship. In: Cretaceous–Tertiary Mass Extinctions: Biotic and Environmental Changes (MacLeod N, Keller G, editors). WW Norton. pp. 85–138. ISBN 978-0-393-96657-2.
- ^ a b Keller G, Adatte T, Stinnesbeck W, Rebolledo-Vieyra, Fucugauchi JU, Kramar U, Stüben D; Adatte; Stinnesbeck; Rebolledo-Vieyra; Urrutia Fucugauchi; Kramar; Stüben (2004). "Chicxulub impact predates the K–T boundary mass extinction". PNAS 101 (11): 3753–3758. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.3753K.doi:10.1073/pnas.0400396101. PMC 374316. PMID 15004276.
- ^ Galeotti S, Bellagamba M, Kaminski MA, and Montanari A (2002). "Deep-sea benthic foraminiferal recolonisation following a volcaniclastic event in the lower Campanian of the Scaglia Rossa Formation (Umbria-Marche Basin, central Italy)" (PDF). Marine Micropaleontology 44: 57–76. doi:10.1016/s0377-8398(01)00037-8. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ Kuhnt W, Collins ES; Collins (1996). "8. Cretaceous to Paleogene benthic foraminifers from the Iberia abyssal plain" (PDF). Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program149: 203–216. doi:10.2973/odp.proc.sr.149.254.1996. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ Coles, GP; Ayress MA; Whatley RC (1990). "A comparison of North Atlantic and 20 Pacific deep-sea Ostracoda". In RC Whatley and C Maybury. Ostracoda and global events. Chapman & Hall. pp. 287–305. ISBN 978-0-442-31167-4.
- ^ Brouwers EM, De Deckker P; Deckker (1993). "Late Maastrichtian and Danian Ostracode Faunas from Northern Alaska: Reconstructions of Environment and Paleogeography". PALAIOS 8 (2): 140–154. doi:10.2307/3515168.JSTOR 3515168.
- ^ Vescsei A, Moussavian E; Moussavian (1997). "Paleocene reefs on the Maiella Platform Margin, Italy: An example of the effects of the cretaceous/tertiary boundary events on reefs and carbonate platforms". Facies36 (1): 123–139. doi:10.1007/BF02536880.
- ^ Rosen BR, Turnšek D (1989). Jell A; Pickett JW, eds. "Extinction patterns and biogeography of scleractinian corals across the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary".Memoir of the Association of Australasian Paleontology. Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Fossil Cnidaria including Archaeocyatha and Spongiomorphs (Brisbane, Queensland) (8): 355–370.
- ^ Ward PD, Kennedy WJ, MacLeod KG, Mount JF; Kennedy; MacLeod; Mount (1991). "Ammonite and inoceramid bivalve extinction patterns in Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary sections of the Biscay region (southwestern France, northern Spain)". Geology 19 (12): 1181–1184.Bibcode:1991Geo....19.1181W. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<1181:AAIBEP>2.3.CO;2.
- ^ Harries PJ, Johnson KR, Cobban WA, Nichols DJ; Johnson; Cobban; Nichols (2002). "Marine Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary section in southwestern South Dakota: Comment and Reply". Geology 30 (10): 954–955.Bibcode:2002Geo....30..954H. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0955:MCTBSI>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
- ^ Neraudeau D, Thierry J, Moreau P (1997). "Variation in echinoid biodiversity during the Cenomanian–early Turonian transgressive episode in Charentes (France)". Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 168: 51–61.
- ^ Raup DM and Jablonski D (1993). "Geography of end-Cretaceous marine bivalve extinctions". Science 260 (5110): 971–973.Bibcode:1993Sci...260..971R. doi:10.1126/science.11537491.PMID 11537491.
- ^ MacLeod KG (1994). "Extinction of Inoceramid Bivalves in Maastrichtian Strata of the Bay of Biscay Region of France and Spain". Journal of Paleontology 68(5): 1048–1066.
- ^ Patterson, C (1993). Osteichthyes: Teleostei. In: The Fossil Record 2 (Benton, MJ, editor). Springer. pp. 621–656. ISBN 0-412-39380-8.
- ^ Zinsmeister WJ (1 May 1998). "Discovery of fish mortality horizon at the K–T boundary on Seymour Island: Re-evaluation of events at the end of the Cretaceous". Journal of Paleontology 72 (3): 556–571. Retrieved2













No comments:
Post a Comment