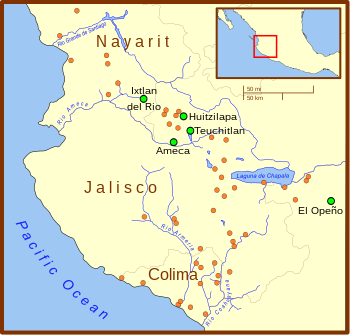
Description[edit]
The shaft tomb tradition is thought to have developed around 300 BCE.[6] Some shaft tombs predate the tradition by more than 1000 years – for example, the shaft tomb at El Opeño in Michoacán has been dated to 1500 BCE but is linked to Central, rather than Western, Mexico. Like much else concerning the tradition, its origins are not well understood, although the valleys around Tequila, Jalisco, which include the archaeological sites of Huitzilapa and Teuchitlan, constitute its "undisputed core".[7] The tradition lasted until at least 300 CE although there is not wide agreement on the end date.[8]
The Western Mexico shaft tombs are characterized by a vertical or nearly vertical shaft, dug 3 to 20 metres down into what is often underlying volcanic tuff. The base of the shaft opens into one or two (occasionally more) horizontal chambers, perhaps 4 by 4 metres (varying considerably), with a low ceiling. The shaft tombs were often associated with an overlying building.
Multiple burials are found in each chamber and evidence indicates that the tombs were used for families or lineages over time.[9] The labor involved in the creation of the shaft tombs along with the number and quality of the grave goods indicate that the tombs were used exclusively by the society's elites,[10] and demonstrate that the shaft tomb cultures were highly stratified at this early date.
The sites of El Opeño and La Campana in Colima feature some shaft tombs, and are often associated with the Capacha culture.
No comments:
Post a Comment